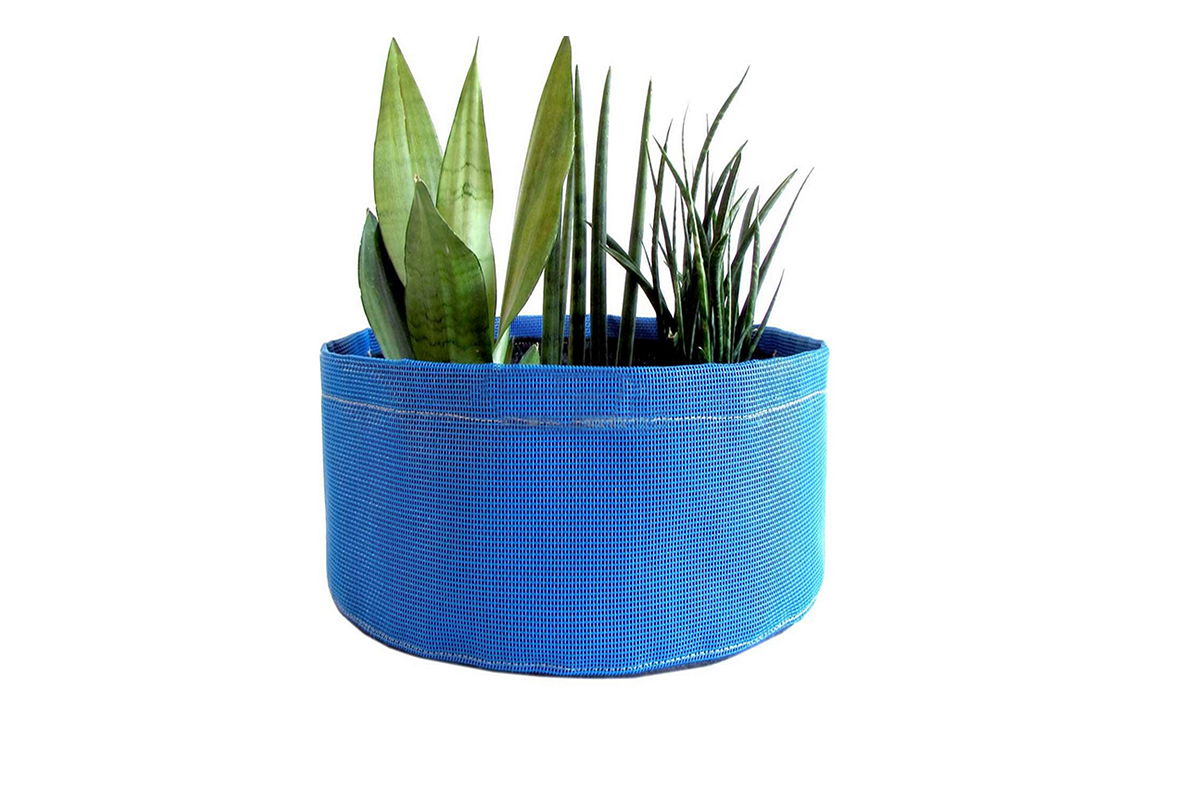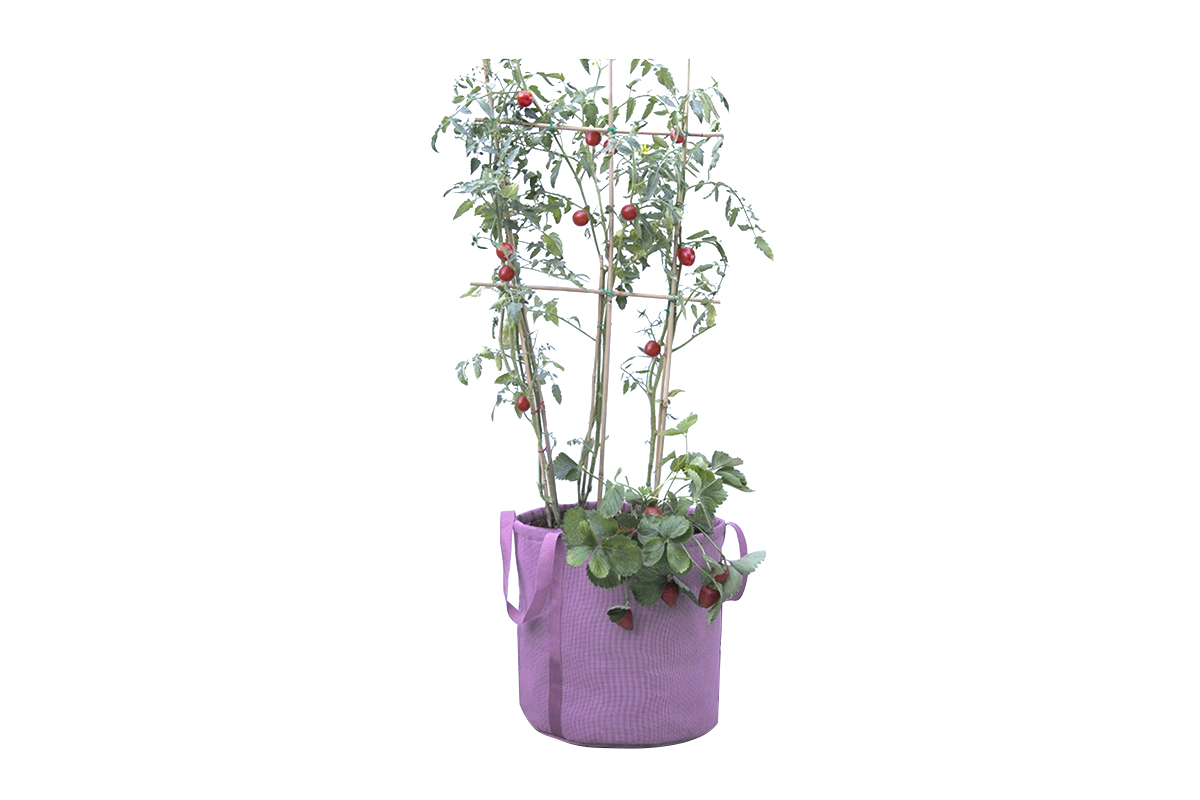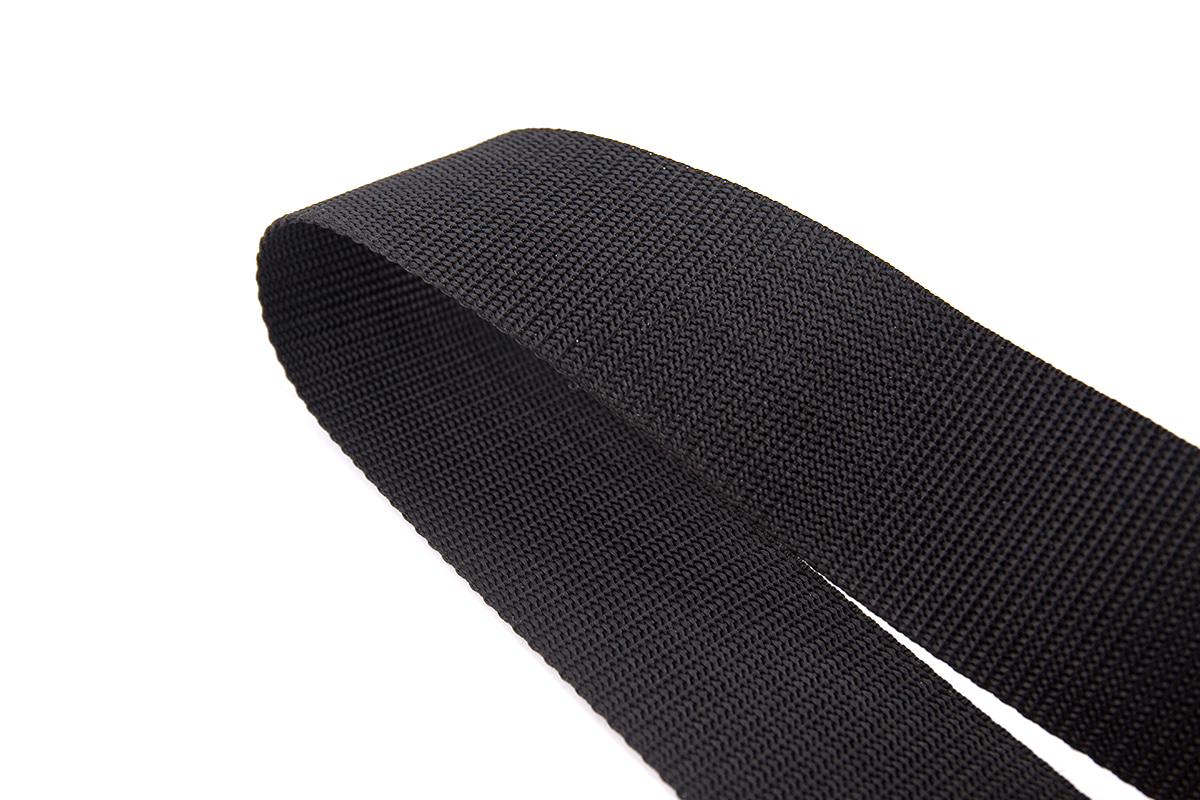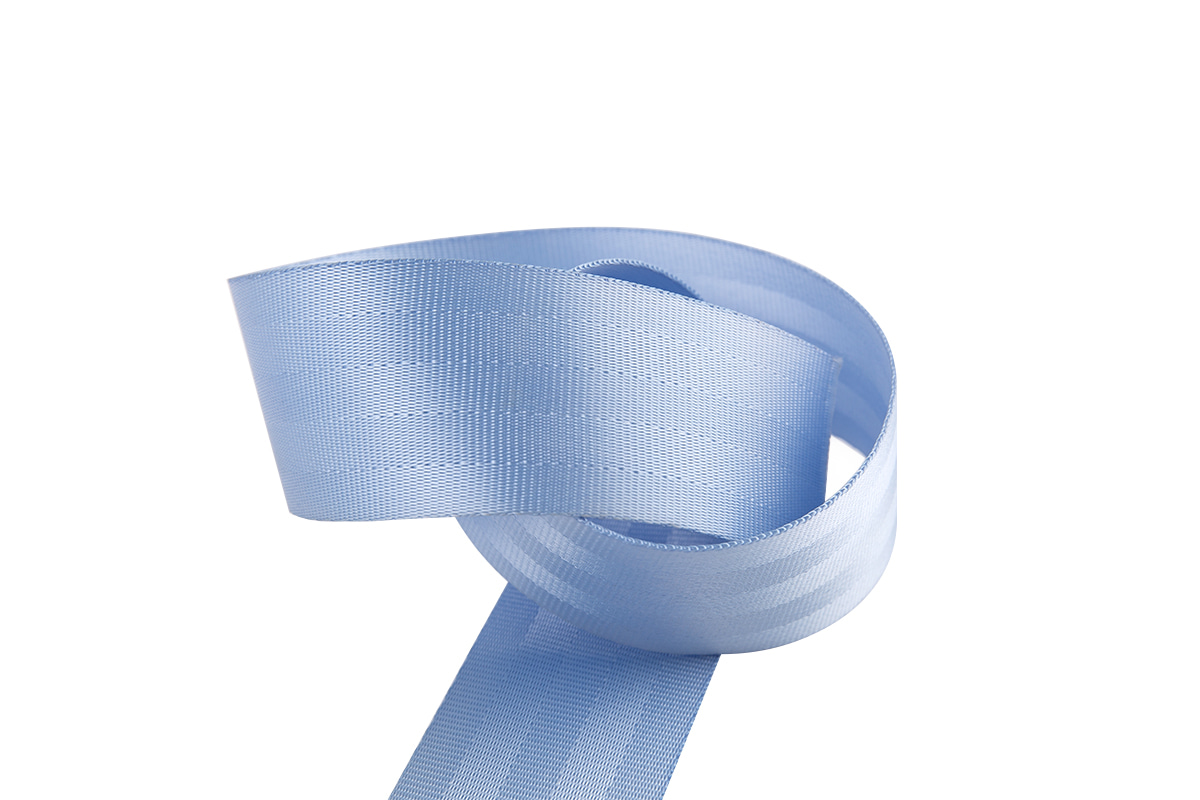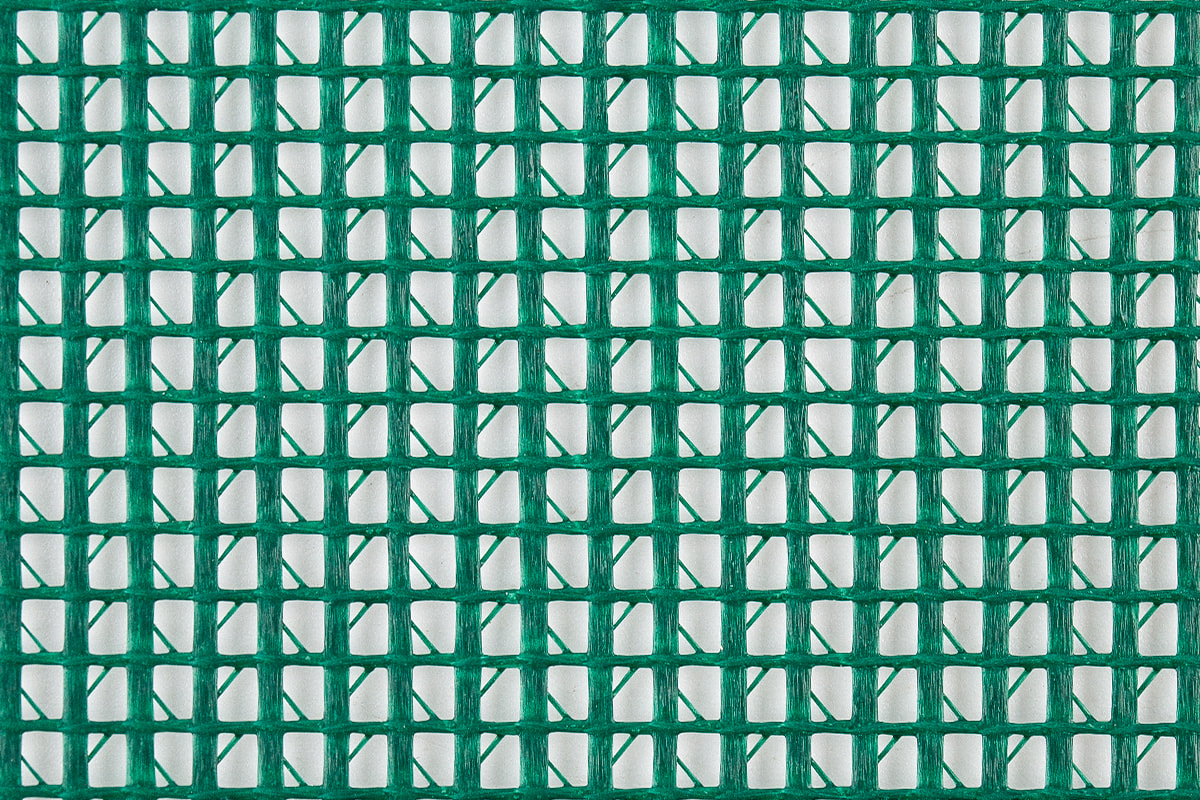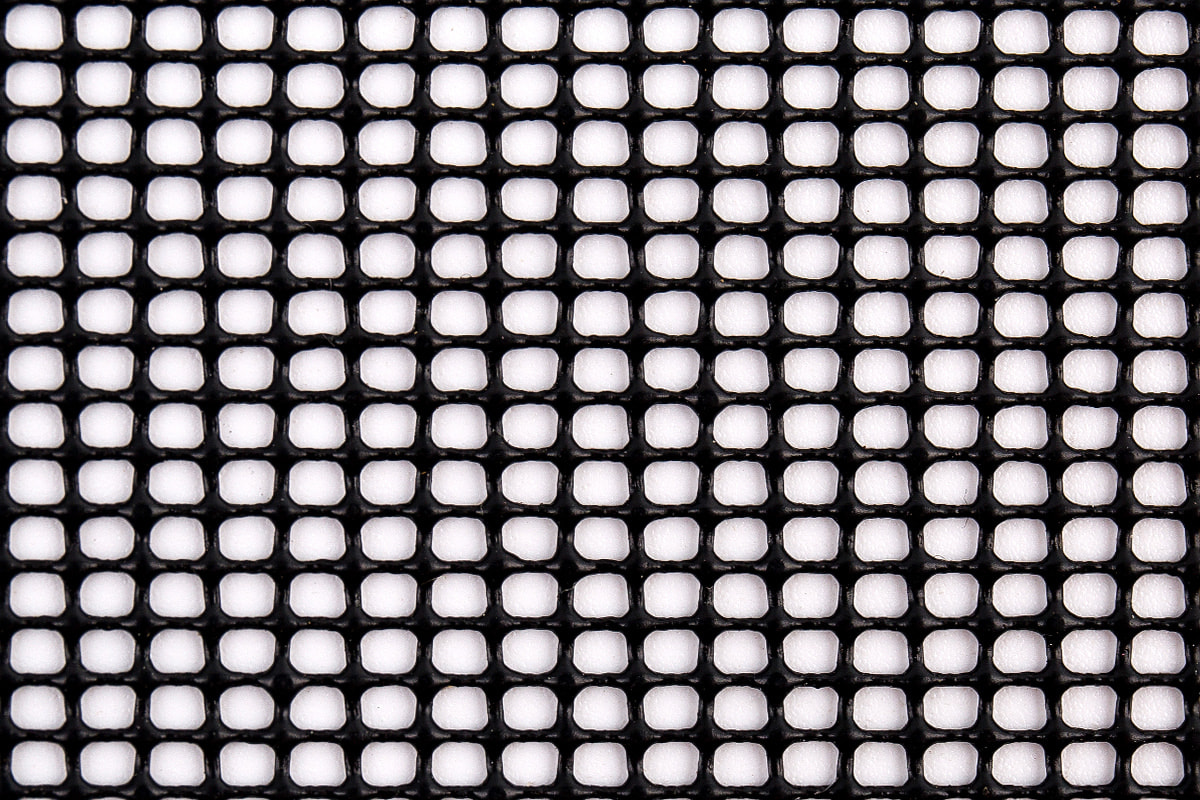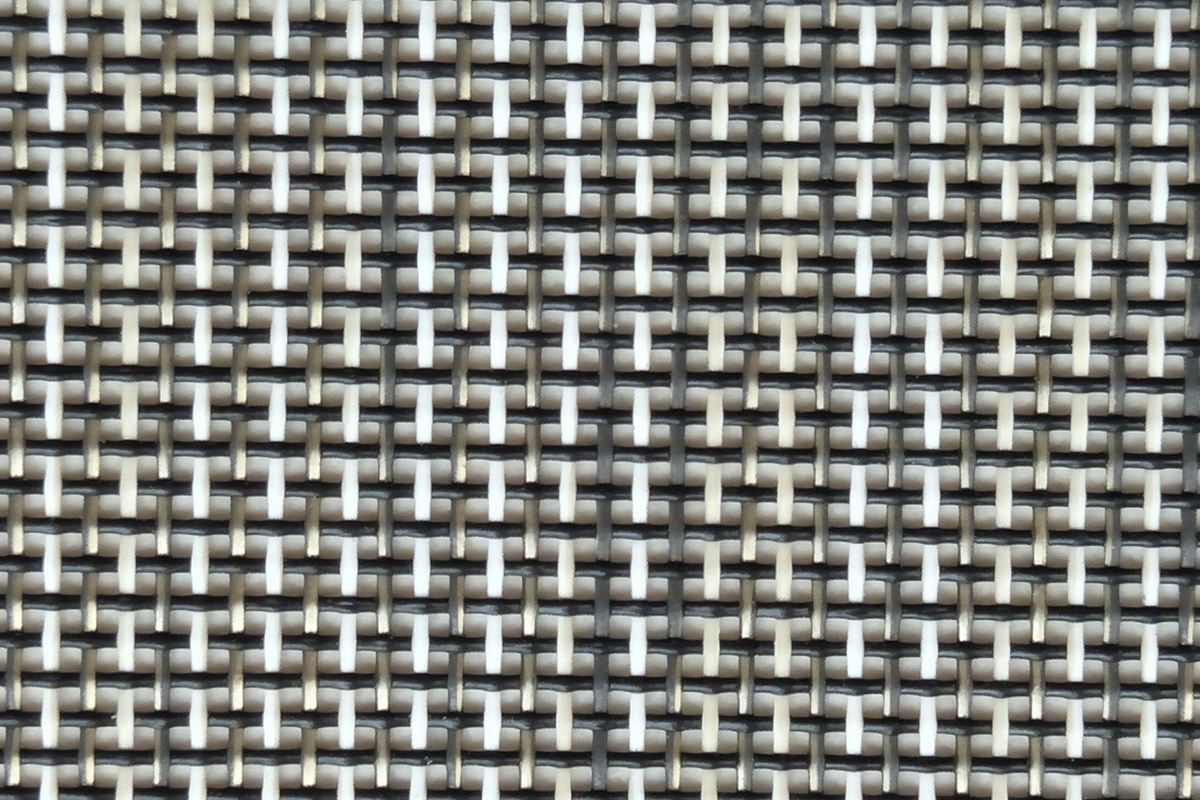
PVC mesh fabric is widely used across various industries due to its strength, durability, and versatility. It is commonly employed in applications ranging from industrial use to fashion and outdoor gear. However, not all PVC mesh fabrics are the same. The materials used in its production play a significant role in determining the fabric's quality and performance.
1. Polyester or Nylon as the Base Fabric
At the core of PVC mesh fabric, you'll often find polyester or nylon. These synthetic fibers are strong, lightweight, and resistant to wear and tear, making them ideal for mesh fabric production. The choice between polyester and nylon generally depends on the desired characteristics of the final product. Polyester is known for its durability and resistance to UV rays, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Nylon, on the other hand, is typically more flexible and resistant to abrasion, which can be useful for items that require a bit more stretch or flexibility.
2. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Coating
The defining feature of PVC mesh fabric is the PVC coating that gives it its unique properties. PVC is a versatile plastic material that is applied to the mesh fabric through a process known as extrusion or coating. The PVC coating serves multiple functions: it makes the fabric waterproof, increases its durability, and provides a protective layer against environmental factors such as UV rays, chemicals, and moisture.
The quality of PVC used can vary, and this affects the final properties of the mesh fabric. High-quality PVC will result in a more durable, flexible, and long-lasting product. PVC also gives the mesh fabric its characteristic glossy finish and contributes to its ability to resist wear from exposure to the elements.
3. Additives and Chemicals
To enhance the performance of PVC mesh fabric, various additives and chemicals are often used in the manufacturing process. These may include plasticizers, stabilizers, flame retardants, and UV inhibitors. Plasticizers are added to improve the flexibility of the PVC coating, allowing the fabric to remain pliable even in colder temperatures. Stabilizers help prevent the PVC from degrading over time due to exposure to sunlight or heat. UV inhibitors protect the fabric from UV radiation, extending its lifespan when used outdoors. Additionally, flame retardants may be included for applications where fire resistance is crucial.
4. Reinforcement Materials
In some cases, PVC mesh fabrics are reinforced with additional materials for added strength. For example, some factories use fiberglass or steel wires to create a more rigid mesh structure. This is especially common in applications where the fabric needs to withstand higher tension or stress, such as in industrial or agricultural settings. Reinforced PVC mesh fabrics offer increased durability and can support heavier loads compared to non-reinforced varieties.
5. Dyes and Pigments
To give PVC mesh fabrics their desired color, dyes and pigments are incorporated into the PVC coating. These are often chosen based on the intended use of the fabric, as certain colors or finishes can be more appropriate for specific applications. For instance, vibrant colors may be used for fashion accessories or decorative items, while neutral or darker tones are often used for industrial applications. The inclusion of pigments not only adds aesthetic appeal but can also contribute to the fabric's UV resistance.
PVC mesh fabric factories rely on a combination of materials to create the final product, including synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon, PVC coatings, various additives, reinforcement materials, and dyes. Each of these materials plays a crucial role in determining the fabric's strength, flexibility, and suitability for different applications. By understanding the materials used in production, consumers can better appreciate the versatility and durability of PVC mesh fabric in a wide range of industries.

 en
en Español
Español